Kissing indiscriminately could kill you, warns a story being shared on social networks. This is because “an outbreak of human papillomavirus” that “kills faster than HIV/Aids” is being spread through kissing in Kenya.
The story goes that several people have already been admitted to hospital in Kenya’s western county of Kisii “after testing positive to the disease”. And the “disease” will soon fan out to the rest of Africa and the world, the article says.
“We are being advised even on Whatsapp groups to avoid kissing and exchanging body fluids,” an unnamed student from Kisii University is quoted as saying.
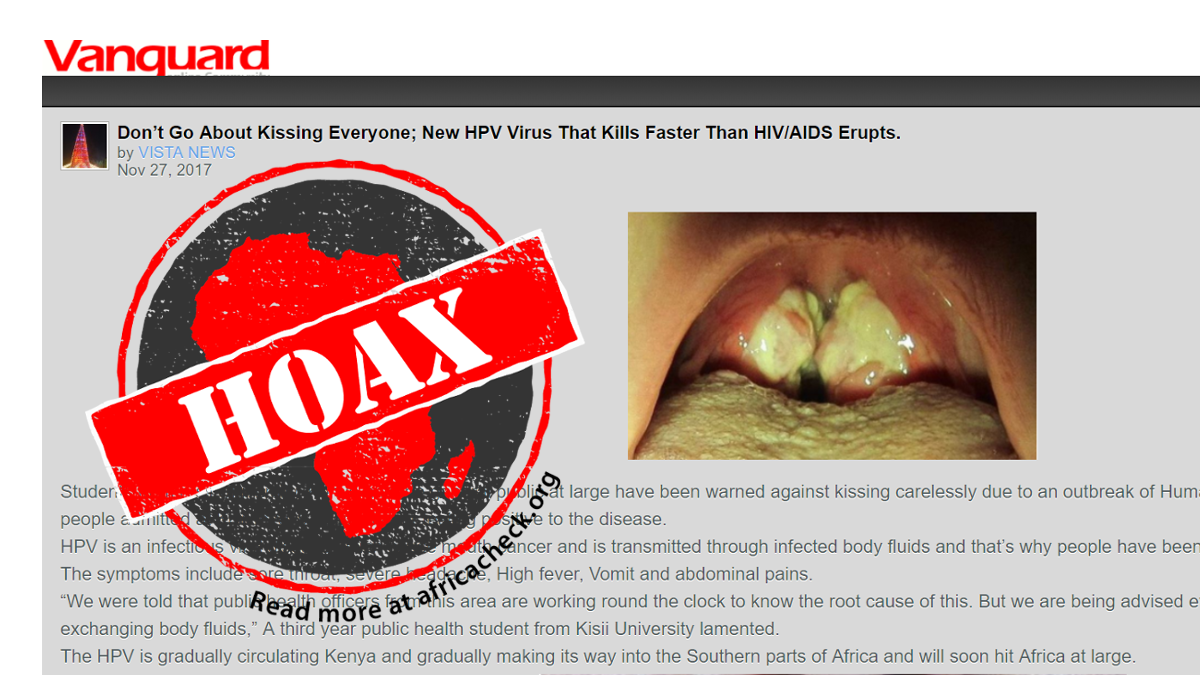
Two pictures in the article supposedly show human papillomavirus (HPV) infections of the lips, tongue and tonsils.
Is a fast-killing strain of HPV being spread by careless kissing? We checked.
“No such outbreak has ever been reported,” Sarah Omache, the Kisii county executive committee member responsible for health, told Africa Check.
Faith Obike, a spokesperson for Kisii Level 5 Hospital, to which patients were allegedly admitted, said their records didn’t show admissions for a HPV “outbreak”.
A reverse image search of the first photo showing infection of the tongue and tonsils revealed it was from the Wikimedia collection of Dr James Heilman, an emergency physician based in British Columbia, Canada.
But on Wikimedia it is identified as showing infectious mononucleosis, or glandular fever. While HPV is commonly spread through body fluids, especially saliva, the virus is not known to cause glandular fever.
“Yes, the photo of the tonsils is of mononucleosis and I took it,” Heilman told Africa Check.
The second image showing sores on lips was traced to a stock photo described as “lips affected by herpes virus”, which Heilman confirmed. “Why would someone use it on a page on HPV?” he asked.
There isn’t a specific disease called HPV, Dr Nelly Mugo, a research scientist at the Kenya Medical Research Institute, told Africa Check. Rather, they are a group of viruses.
“There are more than 100 types of human papillomavirus. Most human beings carry the papillomavirus with no harmful effects,” Mugo said.
The World Health Organization says most HPV infections do not cause symptoms or disease and go away without treatment. But about 15 strains pose a high risk of disease, Mugo said. Two are known to cause the majority of cervical cancer cases.
HPV can infect the mouth during oral sex.
"The same high-risk HPV strain that causes cervical cancer also causes throat and anal cancer,” Dr Ahmed Kalebi, a pathologist and who runs several laboratories on the continent, told Africa Check.
Kalebi said he had not seen any data confirming an “outbreak” of throat cancer in Kenya. “But I do know that we have increased number of cases of throat cancer in recent years and possibly this could be related to high risk HPV because of increased oral sex.”
HPV is almost never transmitted by kissing, said Dr Peter Gichangi, who teaches human anatomy and reproductive health at the University of Nairobi.
“Normal kisses will not lead to infection with HPV. However, if a person infected with oral HPV engages in ‘French’ kissing with an uninfected person, the infection may happen although this is very rare.”
Most HPV infections can be treated, Mugo said, adding that there are also vaccines against the types that increase the risk of cervical cancer.
Because it can take more than 10 years from when a person is infected to when a cancer is detected, during which time an infection with the virus can be treated, it is inaccurate to say HPV can kill faster than HIV, Mugo said.
Gichangi agreed. He said it was “impossible” to be admitted to hospital with “HPV symptoms”. It takes several years for the cancers - oral and others - caused by the virus to develop.
“It is therefore false that HPV kills faster than HIV,” he said. - Vincent Ng’ethe (30/11/2018)
Further reading:
https://africacheck.org/factsheets/guide-verify-images-smartphone/
The story goes that several people have already been admitted to hospital in Kenya’s western county of Kisii “after testing positive to the disease”. And the “disease” will soon fan out to the rest of Africa and the world, the article says.
“We are being advised even on Whatsapp groups to avoid kissing and exchanging body fluids,” an unnamed student from Kisii University is quoted as saying.
Two pictures in the article supposedly show human papillomavirus (HPV) infections of the lips, tongue and tonsils.
Is a fast-killing strain of HPV being spread by careless kissing? We checked.

Kisii county officials unaware of ‘outbreak’
“No such outbreak has ever been reported,” Sarah Omache, the Kisii county executive committee member responsible for health, told Africa Check.
Faith Obike, a spokesperson for Kisii Level 5 Hospital, to which patients were allegedly admitted, said their records didn’t show admissions for a HPV “outbreak”.
What of the images?
A reverse image search of the first photo showing infection of the tongue and tonsils revealed it was from the Wikimedia collection of Dr James Heilman, an emergency physician based in British Columbia, Canada.
But on Wikimedia it is identified as showing infectious mononucleosis, or glandular fever. While HPV is commonly spread through body fluids, especially saliva, the virus is not known to cause glandular fever.
“Yes, the photo of the tonsils is of mononucleosis and I took it,” Heilman told Africa Check.
The second image showing sores on lips was traced to a stock photo described as “lips affected by herpes virus”, which Heilman confirmed. “Why would someone use it on a page on HPV?” he asked.
‘No disease called HPV’
There isn’t a specific disease called HPV, Dr Nelly Mugo, a research scientist at the Kenya Medical Research Institute, told Africa Check. Rather, they are a group of viruses.
“There are more than 100 types of human papillomavirus. Most human beings carry the papillomavirus with no harmful effects,” Mugo said.
The World Health Organization says most HPV infections do not cause symptoms or disease and go away without treatment. But about 15 strains pose a high risk of disease, Mugo said. Two are known to cause the majority of cervical cancer cases.
Oral HPV link to throat cancer
HPV can infect the mouth during oral sex.
"The same high-risk HPV strain that causes cervical cancer also causes throat and anal cancer,” Dr Ahmed Kalebi, a pathologist and who runs several laboratories on the continent, told Africa Check.
Kalebi said he had not seen any data confirming an “outbreak” of throat cancer in Kenya. “But I do know that we have increased number of cases of throat cancer in recent years and possibly this could be related to high risk HPV because of increased oral sex.”
Can kissing cause infection with HPV?
HPV is almost never transmitted by kissing, said Dr Peter Gichangi, who teaches human anatomy and reproductive health at the University of Nairobi.
“Normal kisses will not lead to infection with HPV. However, if a person infected with oral HPV engages in ‘French’ kissing with an uninfected person, the infection may happen although this is very rare.”
Most HPV infections can be treated, Mugo said, adding that there are also vaccines against the types that increase the risk of cervical cancer.
HPV-linked cancers take years to develop
Because it can take more than 10 years from when a person is infected to when a cancer is detected, during which time an infection with the virus can be treated, it is inaccurate to say HPV can kill faster than HIV, Mugo said.
Gichangi agreed. He said it was “impossible” to be admitted to hospital with “HPV symptoms”. It takes several years for the cancers - oral and others - caused by the virus to develop.
“It is therefore false that HPV kills faster than HIV,” he said. - Vincent Ng’ethe (30/11/2018)
Further reading:
https://africacheck.org/factsheets/guide-verify-images-smartphone/
Republish our content for free
For publishers: what to do if your post is rated false
A fact-checker has rated your Facebook or Instagram post as “false”, “altered”, “partly false” or “missing context”. This could have serious consequences. What do you do?
Click on our guide for the steps you should follow.
Publishers guideAfrica Check teams up with Facebook
Africa Check is a partner in Meta's third-party fact-checking programme to help stop the spread of false information on social media.
The content we rate as “false” will be downgraded on Facebook and Instagram. This means fewer people will see it.
You can also help identify false information on Facebook. This guide explains how.





Add new comment